Stem Cell Therapy for Osteoporosis: A New Horizon for Stronger Bones and a Better Life
Osteoporosis is among the most common chronic diseases, where bone gradually loses its density and becomes more fragile, increasing the risk of fractures even with minor injuries. This happens because the body loses bone mass faster than it can regenerate it, disrupting the natural balance of bone renewal.
Traditional treatments—such as dietary supplements, medications, and lifestyle modifications—can slow disease progression but do not rebuild lost bone. This is where stem cell therapy comes in as a groundbreaking approach that combines regenerative medicine with real hope to restore bone structure and improve patients’ quality of life.
How Do Stem Cells Support Bone Health?
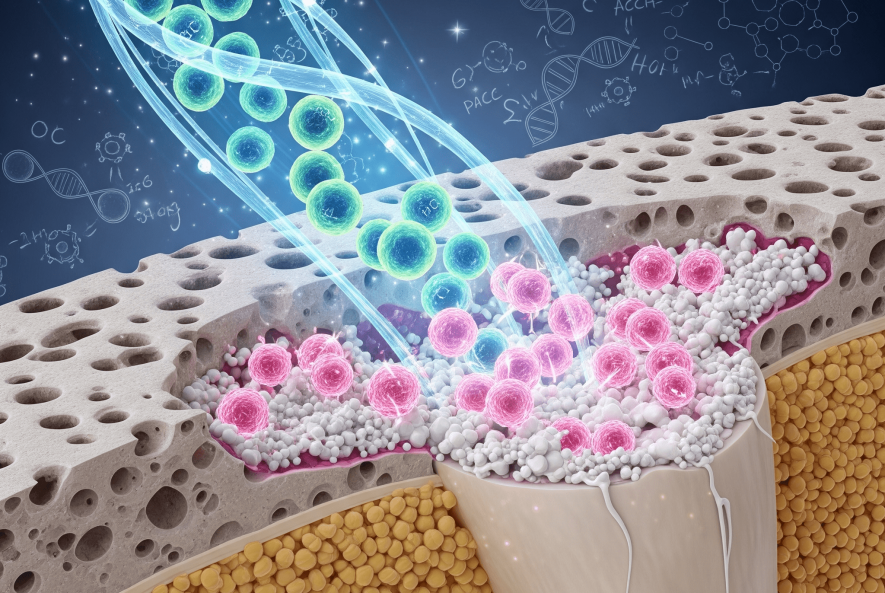
Stem cells have a unique ability to transform into specialized cells, such as osteoblasts (bone-forming cells). In osteoporosis treatment, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are primarily used for their capability to become bone cells and replace lost bone tissue.
Once injected or activated within the body, these cells help regenerate bone through several key mechanisms:
✅ Differentiation into osteoblasts:
They produce a bone matrix rich in collagen and minerals, which supports the formation of new bone and increases bone density.
✅ Activating natural healing processes:
Stem cells release growth factors that stimulate other bone cells, aiding in the repair of damaged tissues.
✅ Reducing inflammation:
Chronic inflammation plays a major role in accelerating bone loss. Stem cells help create an anti-inflammatory environment that supports bone regeneration.
✅ Accelerating fracture healing:
By enhancing the rate and quality of bone healing, this therapy reduces the impact of fractures, especially in older adults.
Types of Stem Cells Used
Currently, the most commonly used type in osteoporosis treatment is:
• Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs): known for their strong potential to differentiate into bone cells and stimulate bone formation.
Advantages of Stem Cell Therapy Over Traditional Methods
🔹 Formation of new bone and restoration of bone density.
🔹 Faster fracture healing and shorter recovery times.
🔹 Reduced pain and improved mobility thanks to increased bone strength and stiffness.
🔹 Minimally invasive procedures, often involving injections rather than major surgeries.
🔹 Reduced dependence on long-term medications and their potential side effects.
Future Directions
Researchers are working to advance this field by:
• Improving techniques for harvesting and processing stem cells.
• Combining stem cells with platelet-rich plasma (PRP) or supportive scaffolds to enhance regeneration.
• Studying the long-term safety and efficacy of these therapies.
• Designing personalized treatment protocols tailored to each patient’s condition.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy represents a revolutionary step in combating osteoporosis. Unlike traditional treatments that merely slow bone loss, it aims to rebuild bone from within and stimulate natural healing.
Thanks to its anti-inflammatory properties and its ability to create new bone tissue, stem cell therapy offers hope for millions of patients seeking stronger bones, better flexibility, and an improved quality of life.
With ongoing scientific advancements, this approach may soon become the leading option in osteoporosis treatment.
